
 PhD student at Peking University.
PhD student at Peking University.I'm a Ph.D. student at the Institute for Artificial Intelligence, Peking University (PKU), advised by Prof. Yitao Liang. I also collaborate closely with Dr. Xiaojian Ma and Prof. Anji Liu. Before joining PKU, I earned my MSc and BA degrees in Control Science and Technology from Beijing Institute of Technology.
My research centers on building open-ended generalist agents, including computer-use agents, embodied game agents, and deep research agents. My core interest lies in building and leveraging large pre-trained Foundation Models (LLMs, VLMs, VLA) to significantly enhance agent generalization capabilities. My research contributions fall into two main categories:
- Agentic Foundation Models: Game-TARS (A generalist game agent trained with a unified, scalable action space anchored to human-aligned native keyboard-mouse inputs), UI-TARS-2 and UI-TARS-1.5 (An open-source multimodal GUI and Game agent built upon a powerful vision-language model), OmniJARVIS (Hierarchical VLA with latent action space), JARVIS-VLA (A vision-language-action model in open worlds).
- Agentic Workflow: DEPS (Planning Agent), JARVIS-1 (Self-improving Agent with Multimodal Memory), RAT (Open Deep Research Agent), ROCKET-1 (Embodied Agent with GUI action space), ProAgent (Collaborating LLM-based Game Agents).
I expect to graduate in 2026 and am looking for job opportunities in the industry. If you are interested in me, please feel free to contact me.
Warning
Problem: The current name of your GitHub Pages repository ("Solution: Please consider renaming the repository to "
http://".
However, if the current repository name is intended, you can ignore this message by removing "{% include widgets/debug_repo_name.html %}" in index.html.
Action required
Problem: The current root path of this site is "baseurl ("_config.yml.
Solution: Please set the
baseurl in _config.yml to "Education
-
 Peking UniversityInstitute for Artificial Intelligence
Peking UniversityInstitute for Artificial Intelligence
Ph.D. CandidateSep. 2022 - present -
 Beijing Institute of TechnologySchool of Automation
Beijing Institute of TechnologySchool of Automation
M.S. in Control Science and TechnologySep. 2019 - Jul. 2022 -
 Beijing Institute of TechnologySchool of Automation
Beijing Institute of TechnologySchool of Automation
B.Eng. in AutomationSep. 2015 - Jul. 2019
Experience
-
Research InternByteDance Seed.Dec. 2024 - present
-
Research InternAlibaba Inc.May. 2021 - Aug. 2021
Honors & Awards
-
Principal Scholarship in Peking University2025
-
Best Paper Award, ICML 2023 TEACH Workshop2023
-
Chinese National Scholarship2021
-
Outstanding Graduate of Beijing2019
-
Meritorious Winner on American Mathematical Contest In Modeling (MCM)2018
News
Selected Publications (view all )

Game-TARS: Pretrained Foundation Models for Scalable Generalist Multimodal Game Agents
Bytedance Seed
arXiv 2025
We present Game-TARS, a generalist game agent trained with a unified, scalable action space anchored to human-aligned native keyboard–mouse inputs. Unlike API- or GUI-based approaches, this paradigm enables large-scale continual pre-training across heterogeneous domains, including OS, web, and simulation games. Game-TARS is pre-trained on over 500B tokens with diverse trajectories and multimodal data. Key techniques include a decaying continual loss to reduce causal confusion and an efficient Sparse-Thinking strategy that balances reasoning depth and inference cost. Experiments show that Game-TARS achieves about 2 times the success rate over the previous sota model on open-world Minecraft tasks, is close to the generality of fresh humans in unseen web 3d games, and outperforms GPT-5, Gemini-2.5-Pro, and Claude-4-Sonnet in FPS benchmarks. Scaling results on training-time and test-time confirm that the unified action space sustains improvements when scaled to cross-game and multimodal data. Our results demonstrate that simple, scalable action representations combined with large-scale pre-training provide a promising path toward generalist agents with broad problem-solving abilities.
Game-TARS: Pretrained Foundation Models for Scalable Generalist Multimodal Game Agents
Bytedance Seed
arXiv 2025
We present Game-TARS, a generalist game agent trained with a unified, scalable action space anchored to human-aligned native keyboard–mouse inputs. Unlike API- or GUI-based approaches, this paradigm enables large-scale continual pre-training across heterogeneous domains, including OS, web, and simulation games. Game-TARS is pre-trained on over 500B tokens with diverse trajectories and multimodal data. Key techniques include a decaying continual loss to reduce causal confusion and an efficient Sparse-Thinking strategy that balances reasoning depth and inference cost. Experiments show that Game-TARS achieves about 2 times the success rate over the previous sota model on open-world Minecraft tasks, is close to the generality of fresh humans in unseen web 3d games, and outperforms GPT-5, Gemini-2.5-Pro, and Claude-4-Sonnet in FPS benchmarks. Scaling results on training-time and test-time confirm that the unified action space sustains improvements when scaled to cross-game and multimodal data. Our results demonstrate that simple, scalable action representations combined with large-scale pre-training provide a promising path toward generalist agents with broad problem-solving abilities.
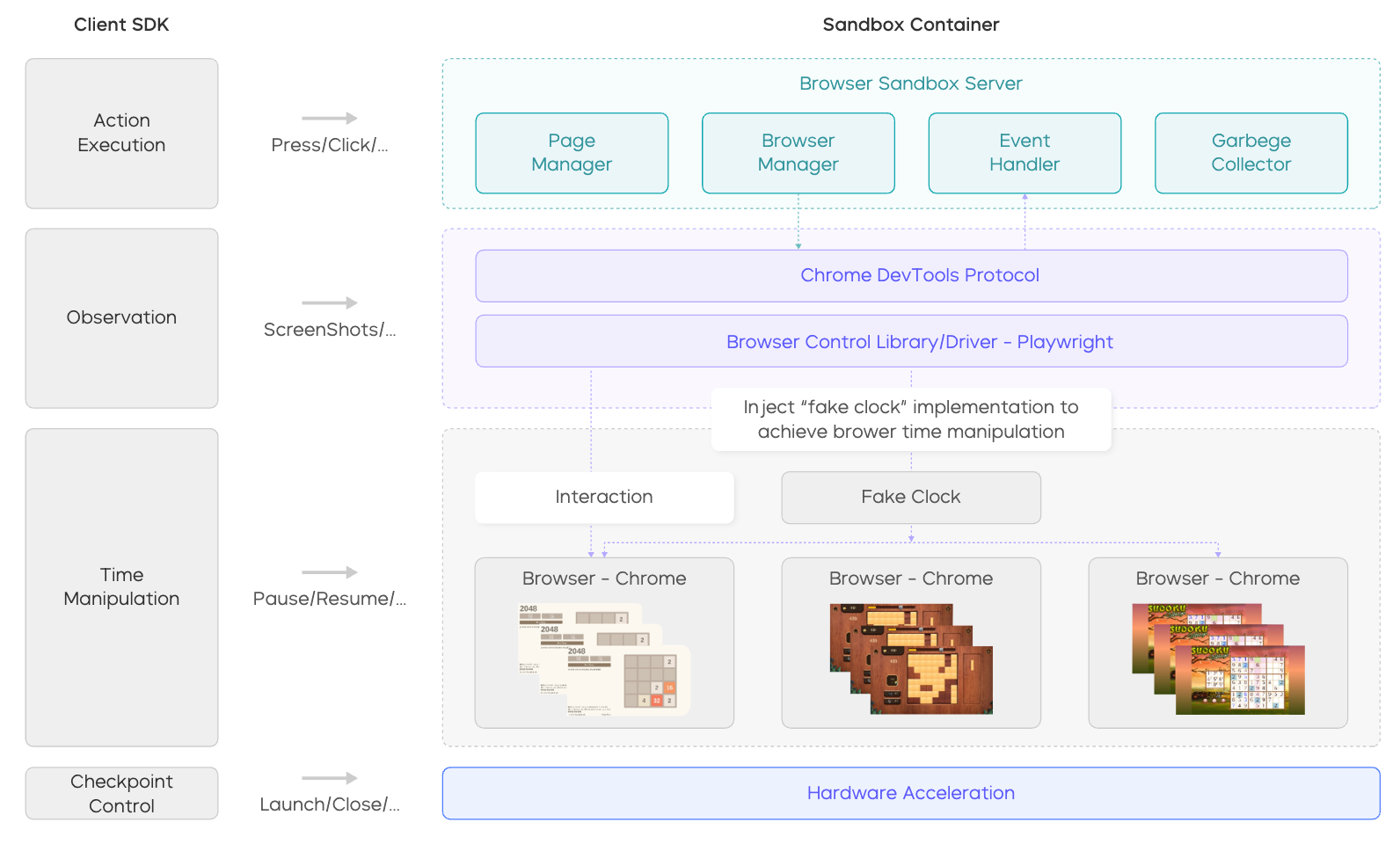
UI-TARS-2 Technical Report: Advancing GUI Agent with Multi-Turn Reinforcement Learning
Bytedance Seed
arXiv 2025
In this technical report, we present UI-TARS-2, a native GUI-centered agent model that addresses these challenges through a systematic training methodology: a data flywheel for scalable data generation, a stabilized multi-turn RL framework, a hybrid GUI environment that integrates file systems and terminals, and a unified sandbox platform for large-scale rollouts. Empirical evaluation demonstrates that UI-TARS-2 achieves significant improvements over its predecessor UI-TARS-1.5. On GUI benchmarks, it reaches 88.2 on Online-Mind2Web, 47.5 on OSWorld, 50.6 on WindowsAgentArena, and 73.3 on AndroidWorld, outperforming strong baselines such as Claude and OpenAI agents...
UI-TARS-2 Technical Report: Advancing GUI Agent with Multi-Turn Reinforcement Learning
Bytedance Seed
arXiv 2025
In this technical report, we present UI-TARS-2, a native GUI-centered agent model that addresses these challenges through a systematic training methodology: a data flywheel for scalable data generation, a stabilized multi-turn RL framework, a hybrid GUI environment that integrates file systems and terminals, and a unified sandbox platform for large-scale rollouts. Empirical evaluation demonstrates that UI-TARS-2 achieves significant improvements over its predecessor UI-TARS-1.5. On GUI benchmarks, it reaches 88.2 on Online-Mind2Web, 47.5 on OSWorld, 50.6 on WindowsAgentArena, and 73.3 on AndroidWorld, outperforming strong baselines such as Claude and OpenAI agents...
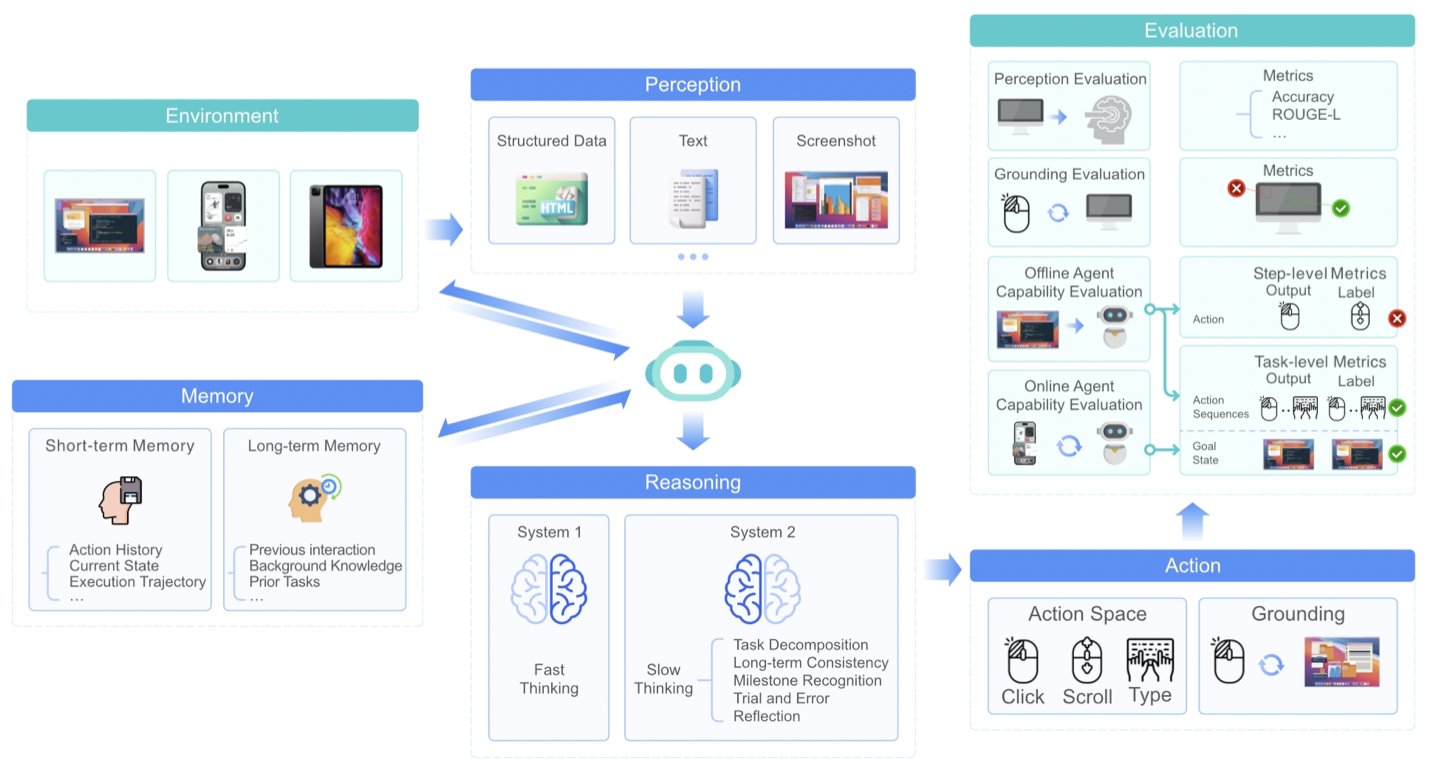
UI-TARS-1.5
Bytedance Seed
arXiv 2025
UI-TARS-1.5 is an open-source multimodal agent built upon a powerful vision-language model. It is capable of effectively performing diverse tasks within virtual worlds. Leveraging the foundational architecture introduced in our recent paper, UI-TARS-1.5 integrates advanced reasoning enabled by reinforcement learning. This allows the model to reason through its thoughts before taking action, significantly enhancing its performance and adaptability, particularly in inference-time scaling. Our new 1.5 version achieves state-of-the-art results across a variety of standard benchmarks, demonstrating strong reasoning capabilities and notable improvements over prior models.
UI-TARS-1.5
Bytedance Seed
arXiv 2025
UI-TARS-1.5 is an open-source multimodal agent built upon a powerful vision-language model. It is capable of effectively performing diverse tasks within virtual worlds. Leveraging the foundational architecture introduced in our recent paper, UI-TARS-1.5 integrates advanced reasoning enabled by reinforcement learning. This allows the model to reason through its thoughts before taking action, significantly enhancing its performance and adaptability, particularly in inference-time scaling. Our new 1.5 version achieves state-of-the-art results across a variety of standard benchmarks, demonstrating strong reasoning capabilities and notable improvements over prior models.
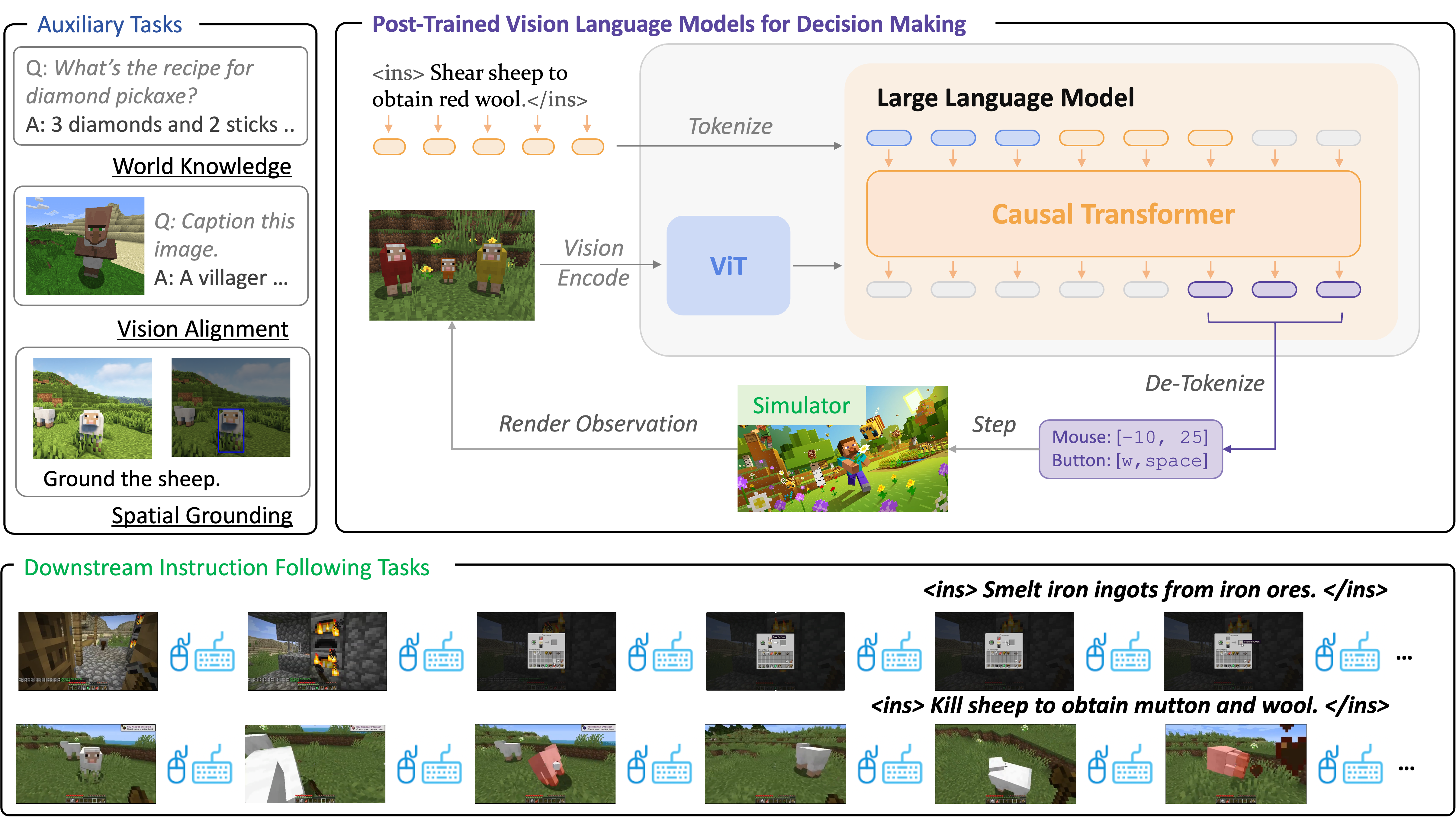
JARVIS-VLA: Post-Training Large-Scale Vision Language Models to Play Visual Games with Keyboards and Mouse
Muyao Li*, Zihao Wang*, Kaichen He, Xiaojian Ma, Yitao Liang (* equal contribution)
ACL Findings 2025
Visual Language Action (VLA) models, pretrained on large-scale web datasets, have shown promise in decision-making tasks. However, previous work has primarily focused on action post-training, often neglecting enhancements to the foundational model itself. In response, we introduce a novel approach, Act from Visual Language Post-Training, which refines Visual Language Models (VLMs) through visual and linguistic guidance in a self-supervised manner. This enhancement improves the models' capabilities in world knowledge, visual recognition, and spatial grounding in open-world environments. Following the above post-training paradigms, we obtain the first VLA models in Minecraft that can follow human instructions on over 1k different atomic tasks, including crafting, smelting, cooking, mining, and killing.
JARVIS-VLA: Post-Training Large-Scale Vision Language Models to Play Visual Games with Keyboards and Mouse
Muyao Li*, Zihao Wang*, Kaichen He, Xiaojian Ma, Yitao Liang (* equal contribution)
ACL Findings 2025
Visual Language Action (VLA) models, pretrained on large-scale web datasets, have shown promise in decision-making tasks. However, previous work has primarily focused on action post-training, often neglecting enhancements to the foundational model itself. In response, we introduce a novel approach, Act from Visual Language Post-Training, which refines Visual Language Models (VLMs) through visual and linguistic guidance in a self-supervised manner. This enhancement improves the models' capabilities in world knowledge, visual recognition, and spatial grounding in open-world environments. Following the above post-training paradigms, we obtain the first VLA models in Minecraft that can follow human instructions on over 1k different atomic tasks, including crafting, smelting, cooking, mining, and killing.
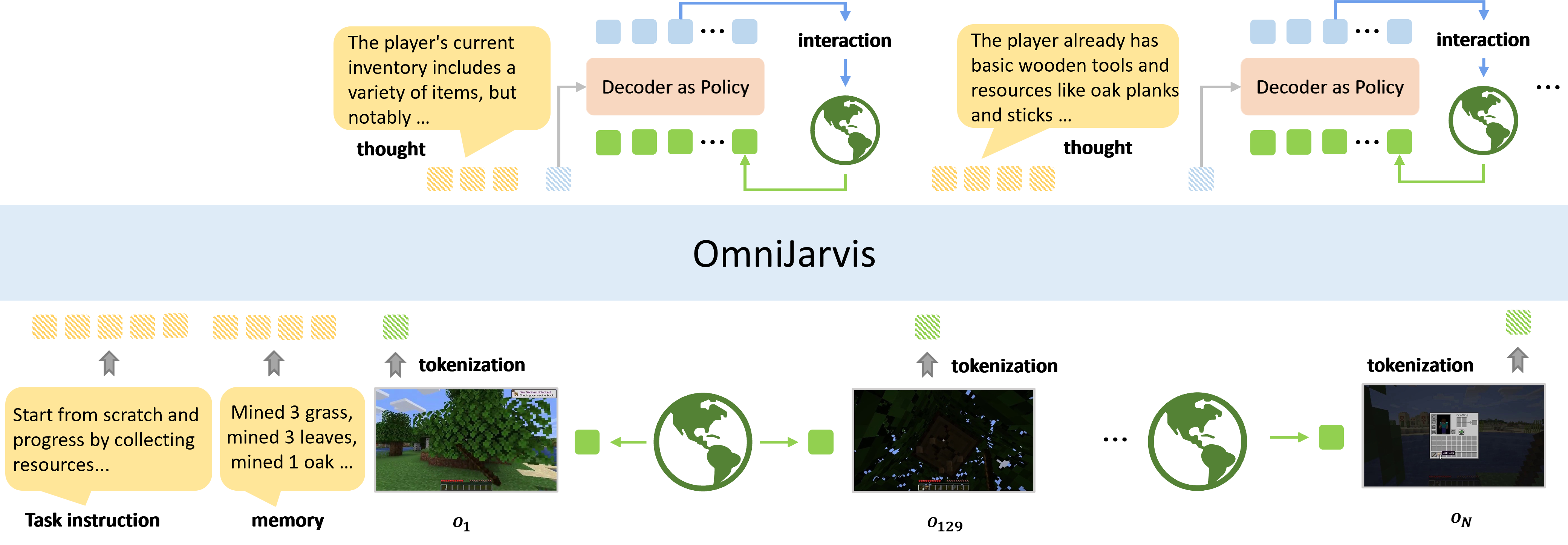
OmniJARVIS: Unified Vision-Language-Action Tokenization Enables Open-World Instruction Following Agents
Zihao Wang, Shaofei Cai, Zhancun Mu, Haowei Lin, Ceyao Zhang, Xuejie Liu, Qing Li, Anji Liu, Xiaojian Ma, Yitao Liang
NeurIPS 2024
An end-to-end open-ended agent based on Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models with self-supervised behavior tokenizer, that can answer questions and follow instructions in open-world Minecraft.
OmniJARVIS: Unified Vision-Language-Action Tokenization Enables Open-World Instruction Following Agents
Zihao Wang, Shaofei Cai, Zhancun Mu, Haowei Lin, Ceyao Zhang, Xuejie Liu, Qing Li, Anji Liu, Xiaojian Ma, Yitao Liang
NeurIPS 2024
An end-to-end open-ended agent based on Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models with self-supervised behavior tokenizer, that can answer questions and follow instructions in open-world Minecraft.
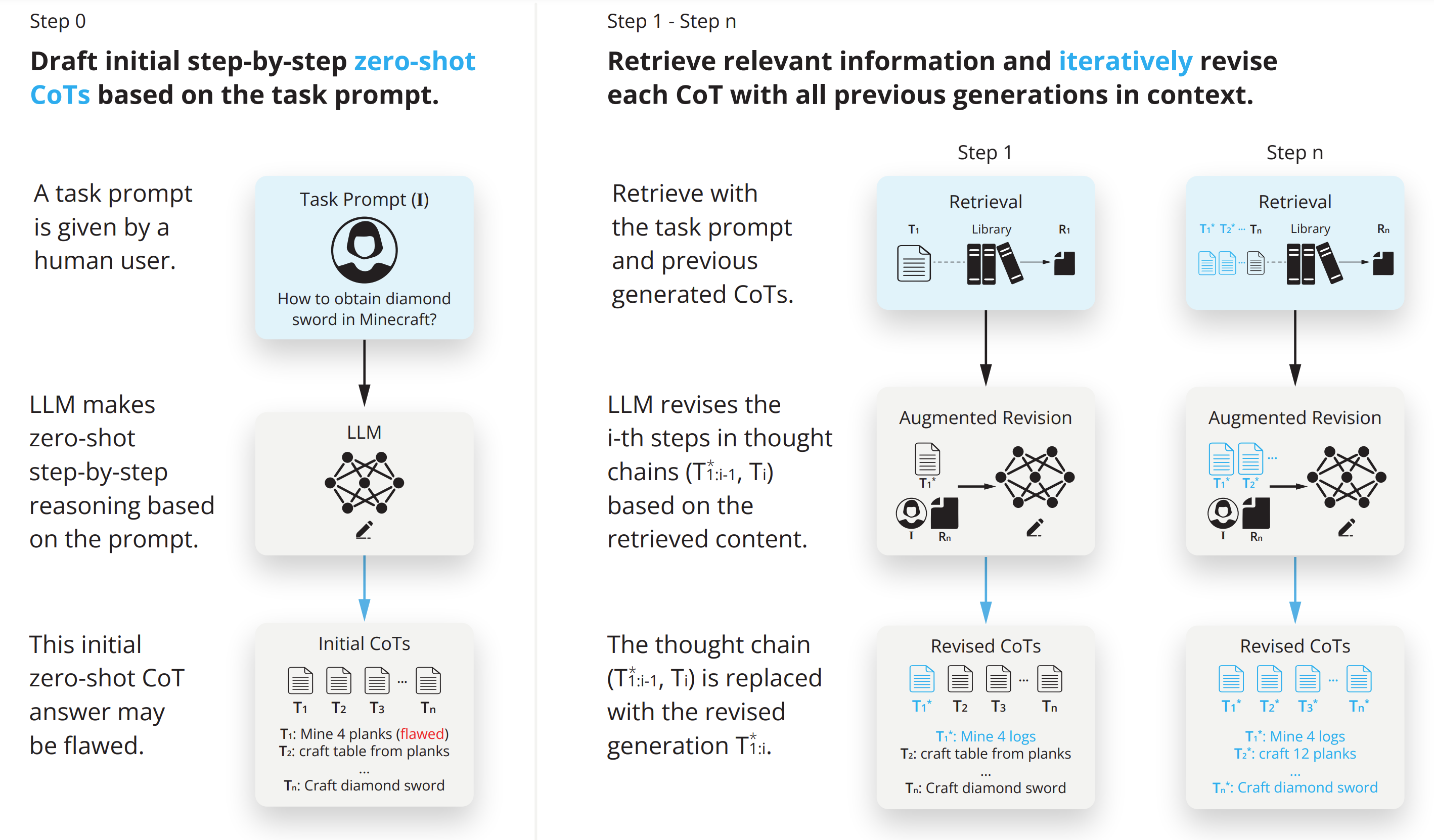
RAT: Retrieval Augmented Thoughts Elicit Context-Aware Reasoning in Long-Horizon Generation
Zihao Wang, Anji Liu, Haowei Lin, Jiaqi Li, Xiaojian Ma, Yitao Liang
NeurIPS Workshop 2024
An agent with retrieval-augmented thought that can conduct code generation, math reasoning, embodied planning and open-ended question answering.
RAT: Retrieval Augmented Thoughts Elicit Context-Aware Reasoning in Long-Horizon Generation
Zihao Wang, Anji Liu, Haowei Lin, Jiaqi Li, Xiaojian Ma, Yitao Liang
NeurIPS Workshop 2024
An agent with retrieval-augmented thought that can conduct code generation, math reasoning, embodied planning and open-ended question answering.
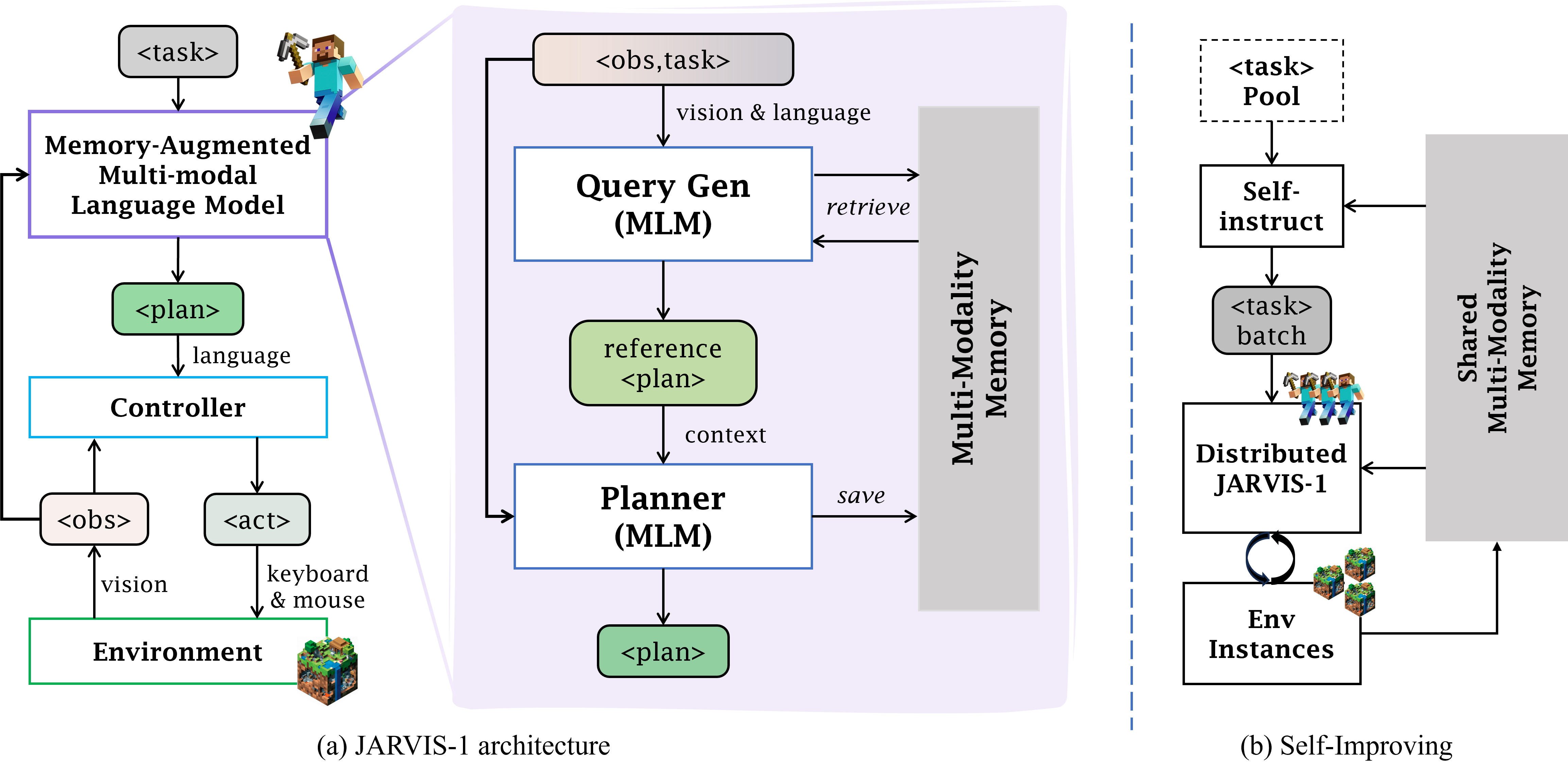
JARVIS-1: Open-World Multi-task Agents with Memory-Augmented Multimodal Language Models
Zihao Wang, Shaofei Cai, Anji Liu, Yonggang Jin, Jinbing Hou, Bowei Zhang, Haowei Lin, Zhaofeng He, Zilong Zheng, Yaodong Yang, Xiaojian Ma, Yitao Liang
T-PAMI 2024
A multi-task agent that can self-improve in open-ended Minecraft and accomplish up to 200+ tasks.
JARVIS-1: Open-World Multi-task Agents with Memory-Augmented Multimodal Language Models
Zihao Wang, Shaofei Cai, Anji Liu, Yonggang Jin, Jinbing Hou, Bowei Zhang, Haowei Lin, Zhaofeng He, Zilong Zheng, Yaodong Yang, Xiaojian Ma, Yitao Liang
T-PAMI 2024
A multi-task agent that can self-improve in open-ended Minecraft and accomplish up to 200+ tasks.
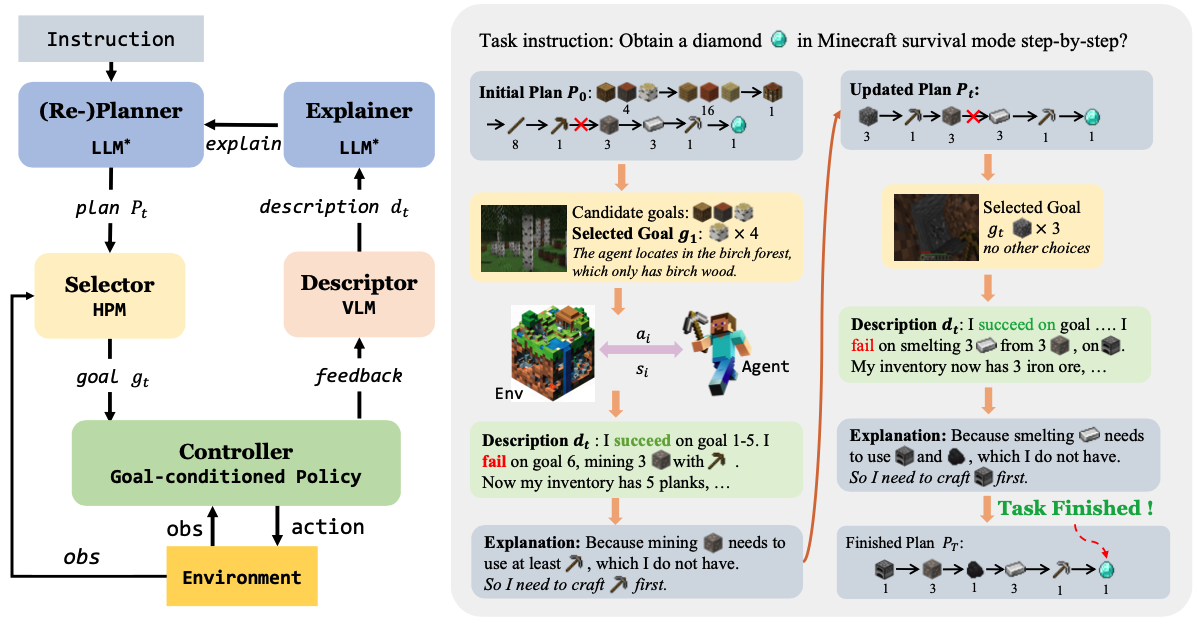
Describe, Explain, Plan and Select: Interactive Planning with Large Language Models Enables Open-World Multi-Task Agents
Zihao Wang, Shaofei Cai, Guanzhou Chen, Anji Liu, Xiaojian Ma, Yitao Liang
NeurIPS 2023 Best Paper Award, ICML 2023 TEACH Workshop
We investigate the challenge of task planning for multi-task embodied agents in open-world environments. We propose"Describe, Explain, Plan and Select"(DEPS), an interactive planning approach based on Large Language Models. DEPS facilitates better error correction on initial LLM-generated plan by integrating description of the plan execution process and providing self-explanation of feedback when encountering failures during the extended planning phases. Furthermore, it includes a goal selector, which is a trainable module that ranks parallel candidate sub-goals based on the estimated steps of completion, consequently refining the initial plan. Our experiments mark the milestone of the first zero-shot multi-task agent that can robustly accomplish 70+ Minecraft tasks and nearly double the overall performances.
Describe, Explain, Plan and Select: Interactive Planning with Large Language Models Enables Open-World Multi-Task Agents
Zihao Wang, Shaofei Cai, Guanzhou Chen, Anji Liu, Xiaojian Ma, Yitao Liang
NeurIPS 2023 Best Paper Award, ICML 2023 TEACH Workshop
We investigate the challenge of task planning for multi-task embodied agents in open-world environments. We propose"Describe, Explain, Plan and Select"(DEPS), an interactive planning approach based on Large Language Models. DEPS facilitates better error correction on initial LLM-generated plan by integrating description of the plan execution process and providing self-explanation of feedback when encountering failures during the extended planning phases. Furthermore, it includes a goal selector, which is a trainable module that ranks parallel candidate sub-goals based on the estimated steps of completion, consequently refining the initial plan. Our experiments mark the milestone of the first zero-shot multi-task agent that can robustly accomplish 70+ Minecraft tasks and nearly double the overall performances.